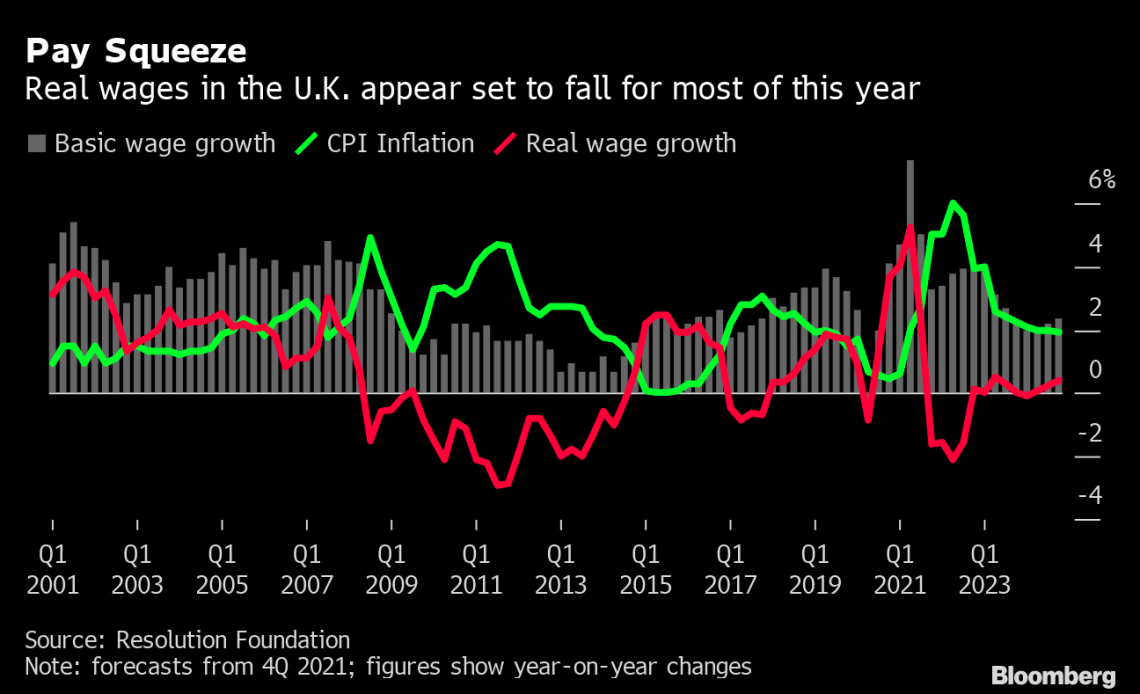
Introduction
The economic landscape of the United Kingdom has been facing a complex array of challenges that have had far-reaching effects on its workforce. One notable issue has been the persistent squeeze on wages across various regions. This article delves into the factors contributing to this wage squeeze and explores the potential implications for workers, businesses, and the broader economy until the end of 2024.
The Wage Squeeze Phenomenon
The wage squeeze refers to a situation where the growth of wages fails to keep up with the rising cost of living, resulting in a reduction of real earnings for workers. This phenomenon has been a recurring concern in the UK, especially in recent years. Despite overall economic growth, many individuals and families have found it increasingly difficult to make ends meet due to stagnant wage growth.
Factors Contributing to the Wage Squeeze
- Inflation: One of the primary drivers of the wage squeeze is inflation. As consumer prices rise, the purchasing power of workers’ wages diminishes, effectively leading to a reduction in their real income. The UK has experienced fluctuations in inflation rates, impacting the affordability of essential goods and services for households.
- Productivity Gap: The UK has grappled with a productivity gap compared to its global counterparts. This gap implies that workers are producing less value per hour worked, limiting the scope for businesses to increase wages without compromising their competitiveness. The productivity challenge has been linked to factors such as inadequate skills training, technological adoption, and infrastructure deficiencies.
- Labor Market Dynamics: The labor market’s supply and demand dynamics play a crucial role in wage determination. In certain sectors and regions, an oversupply of labor relative to job opportunities can depress wage growth. Additionally, the rise of gig economy jobs and non-standard work arrangements has contributed to wage stagnation as these roles often come with lower pay and reduced job security.
- Brexit Uncertainty: The uncertainty surrounding the UK’s exit from the European Union (Brexit) has had implications for wages. The reconfiguration of trade relationships and potential disruptions to the labor market have created an atmosphere of uncertainty, impacting business investments and consequently, wage growth.
- Government Policy and Austerity Measures: Government policies, including austerity measures introduced in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis, have had consequences for public sector wages and services. These policies aimed at reducing public spending have often resulted in frozen or capped wages for public sector workers.
Implications for Workers and the Economy
The prolonged wage squeeze has far-reaching implications for both workers and the broader economy:
- Household Financial Strain: Workers face challenges in maintaining their standard of living as their real wages fail to keep pace with rising costs. This can lead to increased financial strain, reduced savings, and potential difficulties in meeting basic needs.
- Consumer Spending: With limited disposable income, consumers are likely to cut back on discretionary spending, impacting businesses that rely on consumer demand. Reduced consumer spending can slow down economic growth and potentially lead to job losses.
- Income Inequality: Stagnant wages can exacerbate income inequality, as higher-income individuals and business owners may be better positioned to weather economic challenges, while lower-income workers bear the brunt of the wage squeeze.
- Skill and Talent Drain: The lack of competitive wages can result in a brain drain, as skilled workers seek opportunities in other countries where their earning potential is higher.
- Policy Interventions: Policymakers may face increased pressure to address the wage squeeze through measures such as minimum wage adjustments, investment in skills development, and initiatives to stimulate economic growth.
Conclusion
The wage squeeze in many parts of the UK is a multifaceted issue influenced by factors ranging from inflation to labor market dynamics. The repercussions extend beyond individual workers to impact consumer spending, income inequality, and overall economic growth. As the UK navigates these challenges, addressing the wage squeeze will require a comprehensive approach that involves a combination of targeted policies, investments in skills development, and a concerted effort to boost productivity across sectors. Only through a holistic approach can the UK hope to alleviate the wage squeeze and pave the way for sustainable economic prosperity.